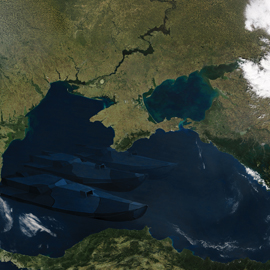
Most discussions of possible United States military operations in the Persian Gulf, should Iran try to prevent maritime traffic from going through the Strait of Hormuz, generally say that while it would not be a cakewalk, it would not be an enormously difficult task either.
But that conventional wisdom is wrong, according to a recent report issued by an independent, non-profit public policy research institute in Washington DC. The report found that the traditional post-Cold War US military ability to project power overseas with few serious challenges to its freedom of action may be rapidly drawing to a close.
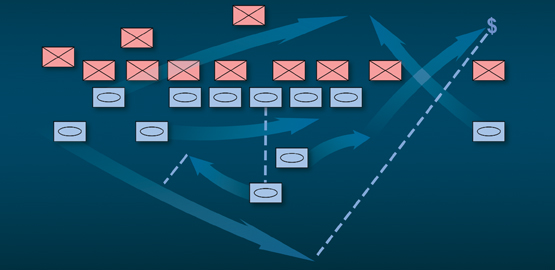
While such conclusions have been voiced before, most notably in regard to capabilities being developed by the People's Republic of China - which is developing an anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) battle network that could constrain the US military's ability to maneuver in the air, sea, undersea, space and cyber-space operating domains - China is hardly the only country that has developed such options.
According to the report published by the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments (CSBA), "Iran, in particular, has been investing in new capabilities that could be used to deter, delay or prevent effective US military operations in the Persian Gulf. Iran's acquisitions of weapons that it could use to deny access to the Gulf, control the flow of oil and gas from the region, and conduct acts of aggression or coercion, are of grave concern to the United States and its security partners."
The report, "Outside-In: Operating from Range to Defeat Iran's Anti-Access and Area-Denial Threats" [1] notes that Iran has been preparing for a possible military confrontation with the United States for decades. Instead of engaging in a direct military competition, which would be pitting its weaknesses against US strengths, Iran has developed an asymmetric "hybrid" A2/AD strategy that mixes advanced technology with guerilla tactics to deny US forces basing access and maritime freedom of maneuver.