Publications
"Nobody does defense policy better than CSBA. Their work on strategic and budgetary topics manages to combine first-rate quality and in-depth research with timeliness and accessibility—which is why so many professionals consider their products indispensable." – Gideon Rose, Editor of Foreign Affairs, 2010-2021
Changing the Game: the Promise of Directed-Energy Weapons
Emerging directed energy technologies have the potential to transition to real-world military capabilities over the next twenty years; and become a particularly promising source of operational advantage for the U.S. military.
The Maturing Revolution in Military Affairs
In 1992, the Office of Net Assessment (ONA), Office of the Secretary of Defense, began circulating an assessment of a prospective late-twentieth-century military-technical revolution (MTR). Soviet military theorists had been discussing the possibility of a third twentieth-century revolution in military affairs (RMA) since the mid-1970s. Written by (then Army Lieutenant Colonel) Andrew F. Krepinevich, ONA’s MTR assessment sought to explore the hypothesis that Soviet theorists were right in predicting that advances in precision munitions, wide-area sensors, and computerized command and control (C2) would bring about fundamental changes in the conduct of war. As Marshal Nikolai Ogarkov, then chief of the Soviet General Staff, observed in 1984, these developments in nonnuclear means of destruction promise to “make it possible to sharply increase (by at least an order of magnitude) the destructive potential of conventional weapons, bringing them closer, so to speak, to weapons of mass destruction in terms of effectiveness.” The Soviets introduced the term “reconnaissance-strike complex” (or “RUK” from the Russian pекогносцировочно-yдарный комплекс) to describe the integration of missiles with precision-guided sub-munitions, area sensors such as the airborne Pave Mover SAR/MTI (synthetic-aperture radar/ moving-target-indicator) radar, and automated C2.
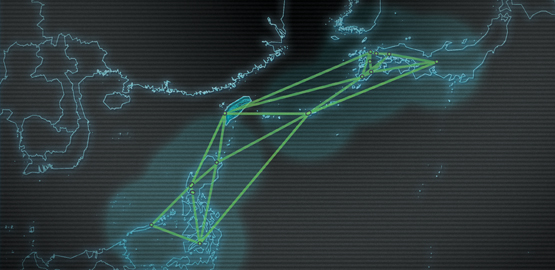
The Implications of China’s Military and Civil Space Programs
Mr. Chairman and Members of the Commission, thank you for inviting me to testify at today’s hearing. I will confine my comments to the Commission’s questions on the overall context of the People’s Republic of China’s (PRC’s) emerging use of orbital systems to support military modernization efforts such as the country’s emerging anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) capabilities in the western Pacific, including the impact of the PRC’s space program on the Chinese concept of Comprehensive National Power (CNP). Regarding the role that the PRC’s space assets might play in U.S.-China conflict scenarios in the 2012-2020 timeframe, I will assess the likelihood of such conflicts occurring and argue that China’s own growing military use of space may constrain their counterspace options in the long run to a greater extent than some of our war gaming has suggested.
Understanding America’s Contested Primacy
In November 2008, the National Intelligence Council released Global Trends 2025 which argued that "the international system–as constructed following the Second World War–will be almost unrecognizable by 2025 owing to the rise of emerging powers, a globalizing economy, a historic transfer of relative wealth and economic power from West to East, and the growing influence of non-state actors...
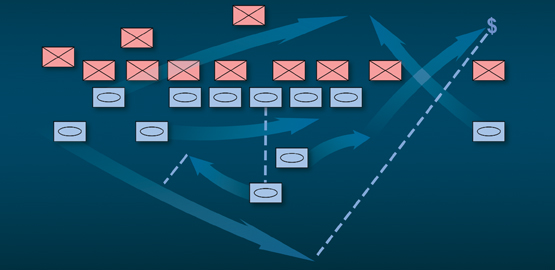
AirSea Battle: A Point-of-Departure Operational Concept
Emerging operational challenges in the Western Pacific require development of a new, integrated concept of operations for U.S. air and sea forces akin to the AirLand Battle of the 1980s
Why AirSea Battle?
For well over half a century, the United States has been a global power with global interests. These interests include (but are not limited to) extending and defending democratic rule, maintaining access to key trading partners and resources, and reassuring those allies and partners who cooperate with the United States in defending common interests. The United States’ ability to project and sustain military power on a large scale has been, and remains, essential to this endeavor.